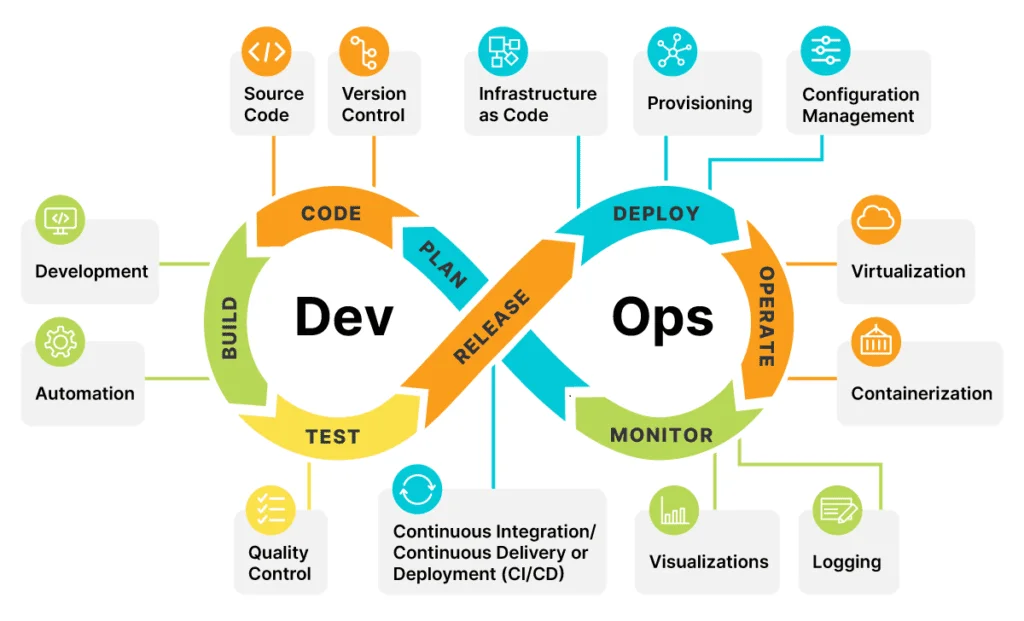
Introduction
Begin with the daily disorder that is the management of a contemporary company, the headache of handling information that is spread out over many spreadsheets, different accounting software, and messy inventory lists. The lack of communication between departments creates an environment where mistakes are made, and confusion reigns.
One of the most significant challenges faced in such a situation is the lack of integration between different systems; thus, an ERP system, which is specifically designed for this purpose, is the answer. The article will go through an ERP in layperson’s terms, identify its principal parts, and elaborate on the strong advantages it can offer any company in terms of smooth operation and sustainable growth.
What Does ERP Stand For?
Definition of ERP
ERP stands for (Enterprise Resource Planning). In simple terms, an ERP is the central nervous system for an entire organization. Its purpose is to bring together and manage all the main processes a company needs. Include These finance, manufacturing, supply chain, human resources (HR), and sales. An ERP trusts all functions into one system instead of using separate software for each task. This important integration lets departments access the same accurate information. This enables smooth work across the business in real-time.
Importance of ERP in Business
Creating a Single Source of Truth
An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system has one of the greatest benefits in this regard elimination of data silos. Data silos arise when vital information gets isolated, meaning only certain departments can access it while others cannot. Through the use of a central database, an ERP system creates a “single source of truth”. Hence, all people in the company, starting from the warehouse manager ending with the CEO, have access to the same information which is updated all the time. Therefore, the ERP system is a major player in the decrease of errors and misunderstandings.
Driving Efficiency and Better Decision-Making
ERP system has a very positive impact on the overall efficiency of the organization since its main function is to enhance operational efficiency. It takes care of numerous mundane and repetitive tasks, such as invoicing, account reconciliation, and inventory data entry, etc. The result of this automation is that the workers are now free to do more creative and valuable work. Moreover, since all the data is stored in one place, it is very easy for the managers to get instant comprehensive reports and insights. This, in turn, allows them to quickly make and more accurately judge the resource allocation, production forecasting, and strategic planning decisions that would ultimately sustain the growth of the business.
What is an ERP System?
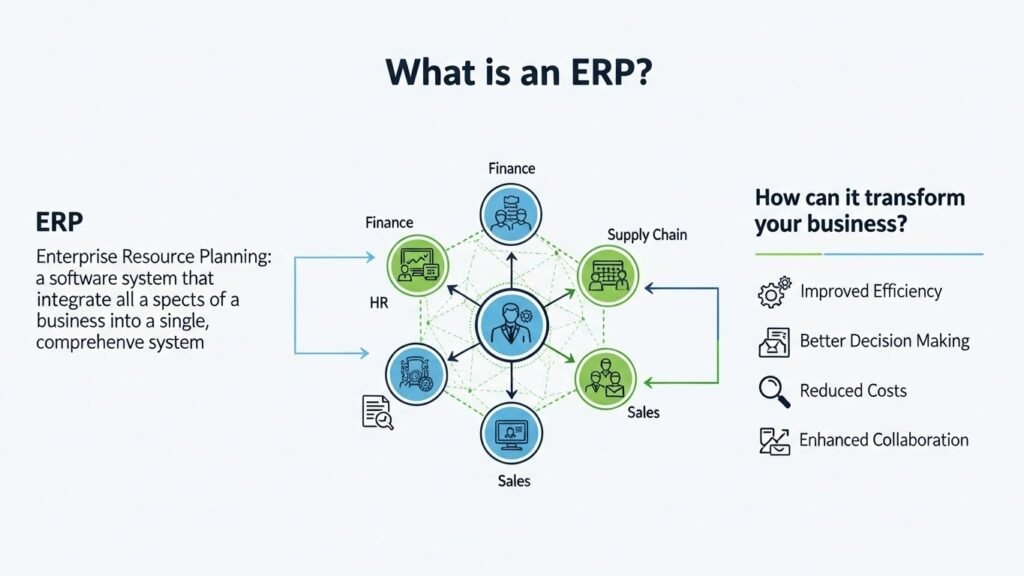
Overview of ERP Systems
An ERP system is often seen as a suite of applications, more popularly known as modules, which are designed to cooperate with each other. Each module deals with a separate business function, yet they all communicate with and access a central, common database. This architecture is what enables true, company-wide integration. Modern ERP solutions offer flexibility, with many businesses choosing Cloud ERP deployment where the software is hosted online and accessed via the internet over traditional on-premise systems, favoring the cloud for its scalability and reduced upfront hardware costs.
Key Components of ERP
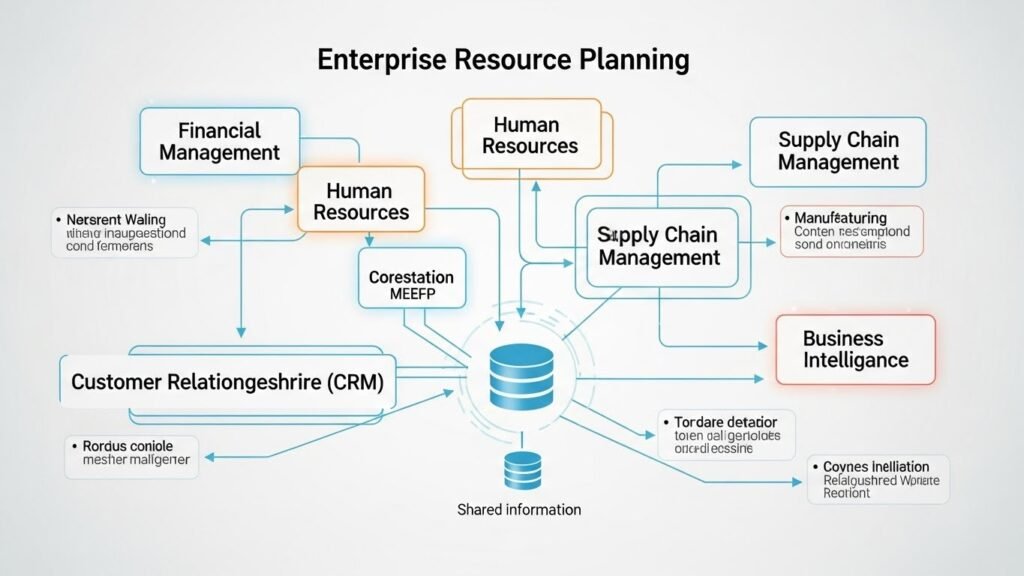
A robust ERP system is comprised of several functional modules, each dedicated to managing a specific part of the business:
Finance and Accounting
This module is the foundation, managing the company’s financial health, including the general ledger, accounts payable and receivable, budgeting, and comprehensive financial reporting.
Sales and Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
This covers the full customer journey, from managing initial leads and quotes to processing sales orders and managing invoicing.
Inventory and Supply Chain Management
This component tracks stock levels in real-time, manages procurement (purchasing), coordinates warehouse operations, and handles all logistics to ensure efficient flow of goods.
Manufacturing
For production companies, this module helps plan and execute the manufacturing process, manage complex Bills of Material (BOMs), and monitor work-in-progress on the factory floor.
Human Resources (HR)
This manages the organization’s most important asset its people handling everything from payroll and benefits administration to recruitment and time-off tracking.
What is an ERP System in Accounting? ERP Systems in Different Domains
In a system that is fully integrated, accounting has ceased to be a solitary, distinct activity. The primary advantage of the ERP system is that it ensures all operational actions get the corresponding financial entries without any manual intervention. Take, for instance, the selling and shipping of a product; the ERP immediately produces the sales invoice, revises the stock figures, and reports the economic effect on the ledger simultaneously. This integration is crucial for the faster monthly closing process, fewer data entry mistakes, and keeping up with the regulations all the time.
ERP for Small Businesses
The notion that ERP systems are only for big firms is still widespread, although it is wrong and dated. However, present-day ERP solutions that scale according to usage and are based on monthly subscriptions have not only made the technology available but also essential for small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) that want to be in the competition. When using ERP, SMBs are able to lower their manual labor expenses since they have automation, while at the same time building up the level of operation of their businesses to be professional and run smoothly, which in turn allows them to be effective in competing with the bigger companies. What is more, a present-day ERP system gives the scalability required to cope with swift growth without its internal systems turning into a mess.
What is an ERP Implementation?
An ERP implementation is the comprehensive process of planning, installing, configuring, migrating data to, and ultimately deploying the new ERP software across an organization. It is more than just a technical installation; it is a critical business project that requires strategic planning and careful coordination to integrate the software with the company’s unique ways of working.
ERP Implementation Process
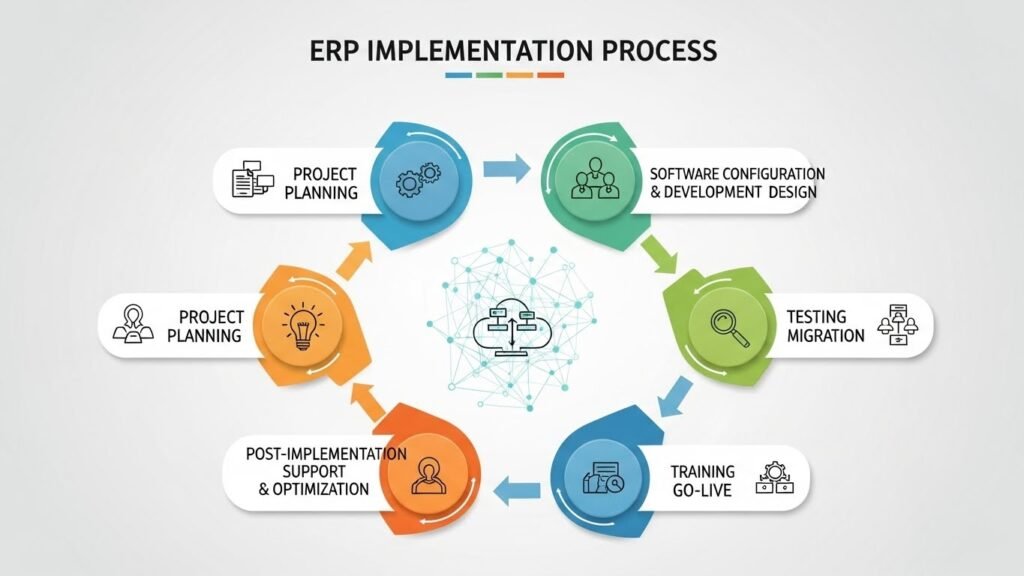
A successful implementation follows several key phases:
- Planning and Analysis: This initial phase involves clearly defining the business goals, selecting the appropriate software, and assembling a dedicated cross-functional project team. It’s essential to map out the company’s existing workflows and identify how the ERP will standardize and improve them.
- Configuration and Customization: Where the software is tailored to the specific needs of the business, configuration involves setting up the system’s built-in rules (like tax codes or user permissions). Customization consists of writing new code or modifying the core system to add unique features not offered out of the box.
- Data Migration and Training: Cleansing and loading of current business data into the system will be in great demand. Most importantly, all employees should be given extensive training according to their roles on how to use the new system efficiently. The adoption of users is the only factor that will determine success and it is the most important one.
- Go-Live and Post-Implementation: Go-live moment is the official transition to the new system. This is immediately followed by a critical post-implementation period where the project team provides intensive support, resolves any initial issues, and optimizes the system’s performance.
ERP Customization Options
ERP Heavy customization can make future software upgrades more complex and expensive. Customizing an ERP may seem appealing to match old processes perfectly, it takes risks. Therefore, most consultants advise prioritizing the system’s built-in formatting options, setting parameters without altering the core code to streamline processes and ensure the system remains easy to maintain and upgrade over time.
ERP Trends and Future
Current ERP Industry Trends
The ERP (enterprise resource planning) industry is undergoing swift changes. The main trend is migrating to Cloud ERP, which is the most convenient and secure option since it allows users to work from anywhere and eradicates the hassle of maintaining local IT infrastructure. Besides, Cloud ERP systems are progressively incorporating AI as well as ML technologies. AI is there for tasks such as predictive analytics, forecasting of the future demand or inventory, and automating complicated financial reconciliations; thus, making the systems more intelligent and proactive. At the same time, the market is also witnessing a growing demand for enterprise solutions tailored for specific industries, which are already set up to comply with the unique regulatory and operational requirements of different sectors like construction, retail, and healthcare.
Odoo ERP as a Leading Solution
A classic instance of an up-to-date, adaptable ERP software is Odoo ERP. Odoo has been on the rise and has grabbed users’ attention mainly due to its modularity and easy-to-use interface. Businesses can begin with only accounting and sales apps; in fact, starting small is a very good option, and then, without any hassle, they can include other modules (like marketing or manufacturing) as their business grows. The open-source nature also plays a vital role in providing a big community ecosystem along with flexibility, thus making Odoo a very attractive choice for organizations that require a system that is powerful and, at the same time, user-friendly for workers to get accustomed to.
Conclusion
The ERP system is not just a large-scale software application; it is a critical enabler of organizational transformation. By integrating various departments, consolidating data, and promoting high levels of automation and efficiency, an ERP equips a company for operations that are smarter and more agile. The implementation of an ERP is a massive undertaking; however, it is one of the most intelligent strategic choices that a firm can make to guarantee its future sustainability and growth in the current competitive and modern marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an example of an ERP system?
There exists a significant number of major players in the ERP market who provide solutions for all types of businesses and industry sectors. Some of the more recognized names are SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics 365, NetSuite, and Odoo. Even though the vendors differ with respect to individual features and the market segments they are targeting, all have the common objective of interconnecting and streamlining the core business processes.
What is the single biggest benefit of using an ERP?
The most significant benefit that an ERP system can give is the attainment of a single, instantaneous view of the whole business. It gets rid of the chaos that comes from using disorganized and obsolete data. An ERP, by guaranteeing that all the divisions operate with the same and correct data, creates better communication, reduces risk, and allows managers to make fast and certain decisions.
Is ERP a type of software or a business strategy?
It is basically dualistic. At the heart of ERP is an advanced software system. Nonetheless, the software can only realize its potential if a well-defined business strategy drives its implementation. If a company decides to implement an ERP system, it will have to go through the steps of examining, normalizing, and fine-tuning its internal processes, which will make the project bring about both technological and business-process change at the same time.